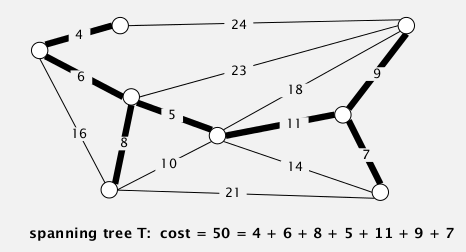
More efficient version of symbol-table where the keys are strings.
1. R-way Tries
Two implementations of symbol tables that we've seen:
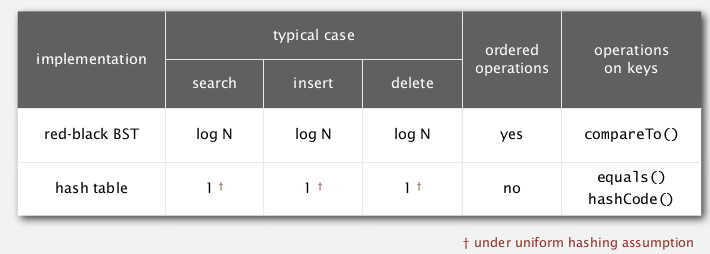
when keys are strings:
(L=string length, N=number of strings, R=radix)
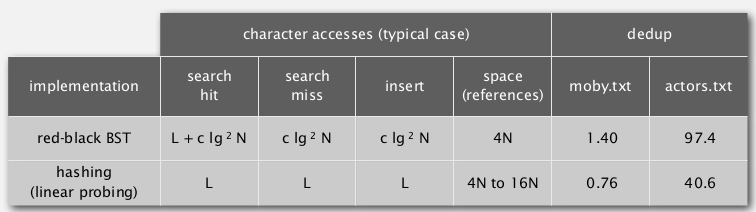
for string keys ⇒ do better by avoiding examing the entire key.
goal: faster than hashtable ...