今天总结一下广度优先搜索(BFS). BFS是树/图的遍历的常用算法之一, 对于没有边权重的图来说可以计算最短路径.
由于树的BFS只是图的BFS的一种特殊情况, 而且比较简单不需要visited标记, 这里只写一下图的BFS好了.
先定义一个Graph类, 这里在每一个节点保存邻居信息:
public class GraphNode{
int val;
List<GraphNode> neighbors;
}
BFS for trees/graphs
图的遍历需要注意不走重复节点, 所以需要一个HashSet(名字叫visited)来保存哪些节点已经访问过了. 需要注意的是, 在把一个节点放进队列queue的时刻就要把它放进visited, 而不是在队列里取出来的时刻再放.
public void BFS(GraphNode start){
LinkedList<GraphNode> q = new LinkedList<GraphNode>();
HasheSet<GraphNode> visited = new HasheSet<GraphNode>();
q.push(start);
visited.add(start);
while(!q.empty()){
GraphNode cur = q.poll();
System.out.println(cur.val);
for(GraphNode next: cur.children){
if(!visited.contains(next)){
q.push(next);
visited.add(next); // mark node as visited when adding to queue!
}
}
}//while
}
BFS with distance
在BFS的同时我们可以记录从start节点到当前node的距离, 方法是把一个距离信息同时入队(封装一个Pair<GraphNode, Integer>), 或者使用一个与queue平行的队列保存距离信息.
在上面的代码中, 加入:
//...
LinkedList<Integer> distq = new LinkedList<Integer>();
distq.push(0);// distance from start to start
//...
// in the while(!q.empty()) loop:
int d = distq.poll();//get distance from start to current node
for(GraphNode next: node.children){
distq.push(d+1);// distance from start to next node
//...
对于Tree的情况来说, 这里的dist其实就是当前节点的深度depth.
properties
性质1:
每个节点node的distance都是node距离起始点start的最短距离.
性质2:
距离start近的节点(depth浅的节点)一定比距离start远的节点早被访问到.
这是对一个树BFS的时候节点的访问顺序:
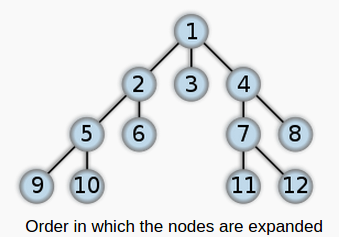
BFS "by layer"
参考上面的性质, 可以一次处理"一层"的节点, "一层"的意思是指所有节点距离start的距离相同. 代码在while循环里不是一次poll一个节点, 而是一次把queue的内容处理完, 然后换新的queue进入下一次while循环. 代码重新写一下:
public void BFS(GraphNode start){
ArrayList<GraphNode> q = new ArrayList<Tree>();
HasheSet<GraphNode> visited = new HasheSet<GraphNode>();
q.push(start);
visited.add(start);
while(!q.empty()){
ArrayList<GraphNode> newq = new ArrayList<Tree>();// create a new queue
for(GraphNode cur: q){// deal with all nodes in the queue
System.out.print(cur.val+", ");// all nodes in q are of the same distance/depth
for(GraphNode next: cur.children)
if(!visited.contains(next))
{ newq.push(next);visited.add(next); }
}
System.out.println();
q = newq;//replace q with newq
}//while
}
以上程序每次打印一行, 第i行包括了距start距离为i的所有节点.
由于这样的话每次不必在队首poll出元素(而是依次处理所有queue的元素), 所以可以改用ArrayList. 此时while循环里的不变量是: 所有q里面的节点距离start的距离都相同.
complexity
假设一个图有N个节点和M条边, BFS会走遍所有节点, 时间是O(N), 然后由于每个节点会检查所有的出边, 最终所有的边都会被检查过, 时间是O(M), 所以BFS的时间复杂度是O(N+M).
队列里面最多可能存放所有节点, 空间复杂度为O(N).
Disqus 留言