Here is a mindmap of the common algorithms and data structures, it can give an overview of the algorithmic terms.
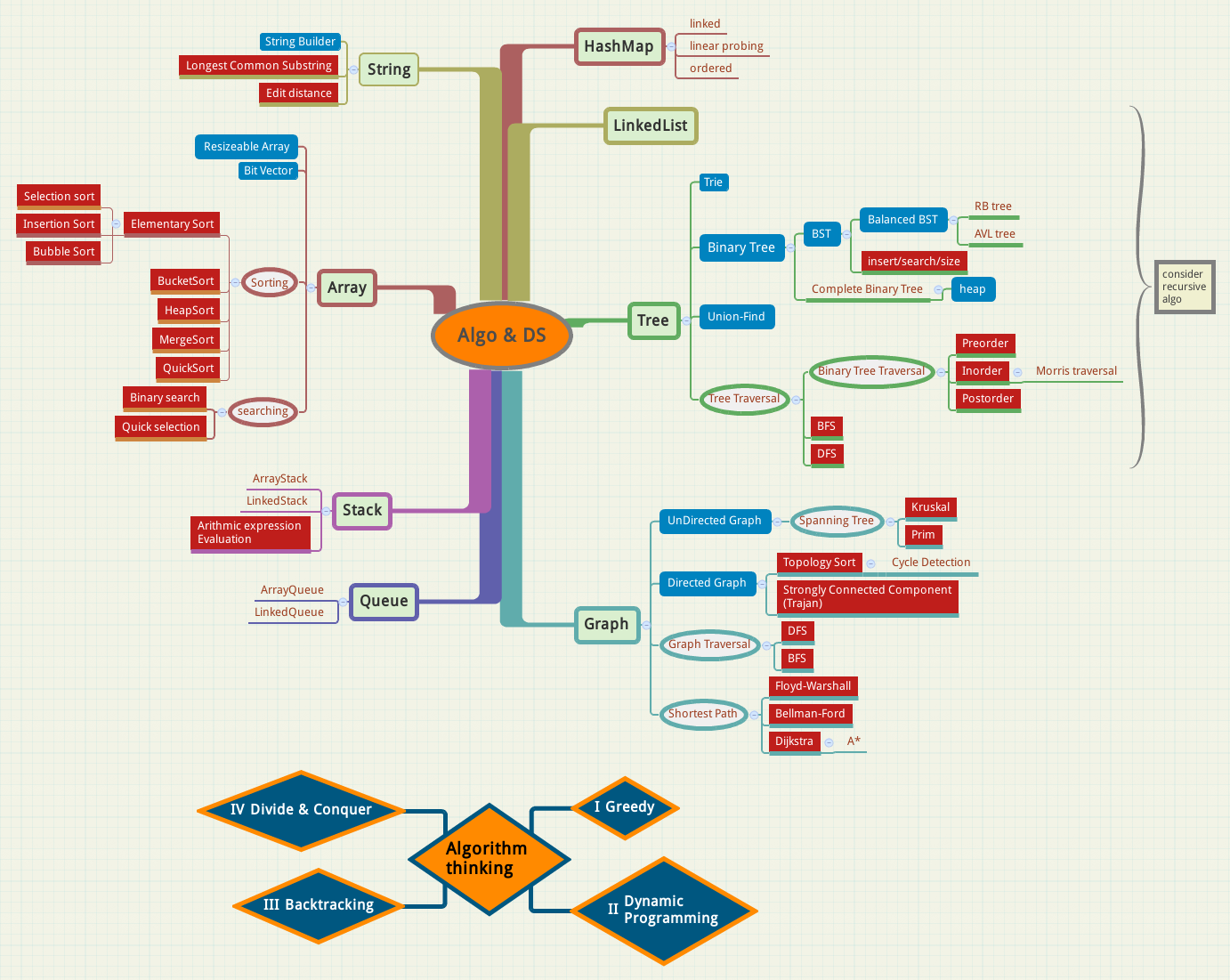
I shall update its content later on. And maybe write some blog entries on some of the items.
This mindmap is drawn using xmind.
Here is a mindmap of the common algorithms and data structures, it can give an overview of the algorithmic terms.

I shall update its content later on. And maybe write some blog entries on some of the items.
This mindmap is drawn using xmind.
Can we do better than BST if we do not need ordered operations ?
(No compare methods, use equals method)
Idea: save items in an array.
Hash function: method for calclulating the array index of a key.
Issues:
Classic space-time tradeoff.
Goal: intersections of geometric objects.
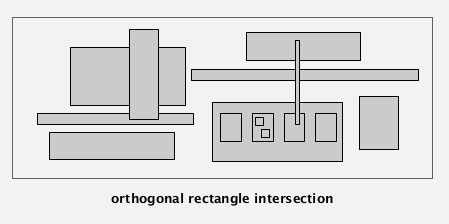
Solution: BST
operations required:
→ find points on an interval

range count
using the rank ...
goal: lgN for insert/search/delete operations (not necessarily binary trees..)
3 algo: 2-3 tree, (left leaning) red-black tree, B-tree
def. 2-3 tree
(BST是锻炼递归代码的好题目)
def. BST
A binary tree where each node has a key:
for every node, the key is larger than all nodes in left subtree, smaller than all nodes in right subtree.
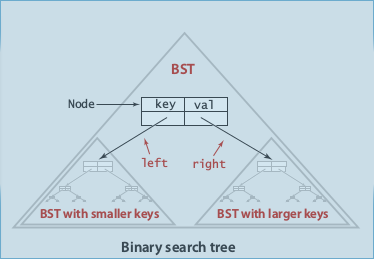
Fields: key, val, left, right
An inner class of BST nodes:
private class ...key-value pair abstraction
Associate a value to a key — generalized array: a[key]=val.
public class ST<Key, Value>{
void put(Key k, Value v);//remove key if value=null ...Collection: data struct for inserting and deleting items (ex. stack and queue).
Priority queue: a special kind of collection — remove largest/smallest element.
API:
public class Max<Kye implements Comparable<Key>>{
public MaxPQ();
public void insert(Key k);
public Key delMax();
public boolean isEmpty();
public ...(maybe best algorithm for sorting.)
Idea:
no larger entry to the left of pivot
no smaller entry to the right of pivot
Two classical sorting algorithms: mergesort, quicksort.
Divide and conquer: top 10 algorithms of the 20th century, invented by von Neumann.
Idea:
Merge:
Goal: a[lo] to a[mid] and a[mid+1] to a ...
rearanging array of size N into ascending order
test client code: Insertion.sort(a);
sort any datatype
callback = reference to executable code
i.e. passing functions as argument to sort() method
sort() function calls object's compareTo() method

→ implement the Comparable interface:
public class XX implements Comparable ...