1 create project sunshine
Created 星期一 06 二月 2017
minSDK vs targetSDK
The minSDK is the lowest SDK level that your app can run on. You can choose what level of devices to support.
By comparison, the targetSDK is NOT a high pass filter -- it’s used only to declare which platform version you've tested your app on.
Enable VT-x and installing kvm
this is necessary for running AVD devices.
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/37087365/how-to-enable-vt-x-in-bios-and-kvm-modules-on-linux
Components of an android app
4 main components of an app:
Activity: responsible for most user interaction- Service
- ContentProvider
- BroadcaseReceiver
Activity
Android keeps the activities in a stack, when press back button → stack pops.
Define the launcher of the activity in manifests/AndroidManifest.xml:
application → activity → intent-filter
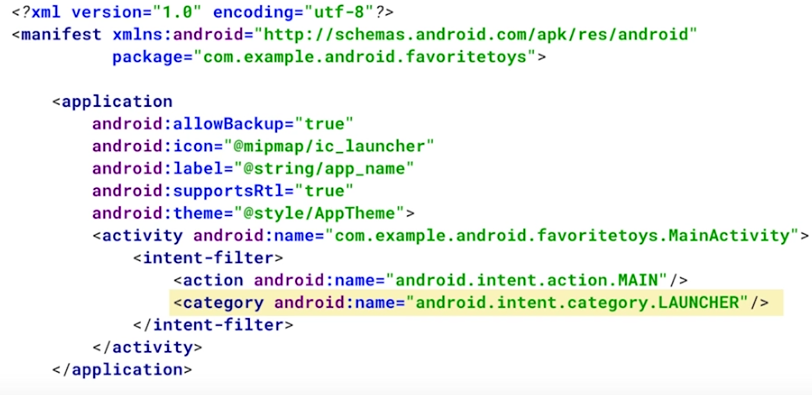
res folder contains layouts/images/values
in res/layout/activity_main.xml: xml file that defines the layout view
Activities and Layouts
An activity is a single focused thing that the user can do. Activities are responsible for creating the window that your application uses to draw and receive events from the system. Activities are written in Java, extending from the Activity class.
An activity creates views to show the user information, and to let the user interact with the activity. Views are a class in the Android UI framework. They occupy a rectangular area on the screen and are responsible for drawing and handling events. An activity determines what views to create (and where to put them), by reading an XML layout file. These XML files, are stored in the res folder inside the folder labeled layouts.
2 types of views
type1: UI components (widgets)
UI components that are often interactive elements.
example: TextView, EditView, Buttom, ImageView,...
most of UI view classes: in android.widgets package https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/package-summary.html
type2: container view
The second are views called "Layout" or "Container" views. They extend from a class called ViewGroup. They are primarily responsible for containing a group of views and determining where they are on screen. Layout views can be nested in one another.
example: LinearLayout, RelativeLayout, ConstraintLayout, ...
relate XML layout to java activities
use xml layout in java activity
in onCreate method of an activity, using the setContentView(R.layout.name_of_layout)
the setContentView method: Android reads your XML file and generates Java objects for each of the tags in your layout file. You can then edit these objects in the Java code by calling methods on the Java objects.
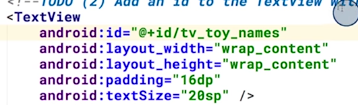
refer to widgets defined in xml in java
in the xml file, give an id to the view:
Disqus 留言