1. Symbol Table API
key-value pair abstraction
- insert a value with a key
- given a key, search for its value
Association array abstraction
Associate a value to a key — generalized array: a[key]=val.
public class ST<Key, Value>{
void put(Key k, Value v);//remove key if value=null
Value get(Key k);//return null if key is absent
void delete(Key k);
boolean contains(Key k);
boolean isEmpty();
int size();
Iterable<Key> keys();//better to return an ordered sequence of keys
}
conventions:
- values are not null
- get() returns null if key not present
- put() can overwrite older value
→ some one-line implementations:
- contains:
return get(k)!=null; - delete:
put(k, null);
Assume keys to be comparable: class ST<Key implements Comparable<Key>, Value>— can thus use compareTo() method.
Else → we can only use the equals() method...
Be careful when implementing the equals method: 坑不少...

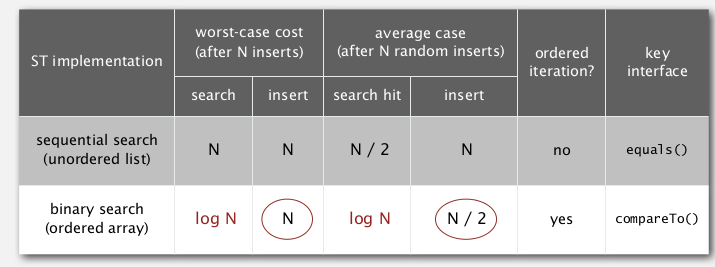
2. Elementary implementations
naive implementations
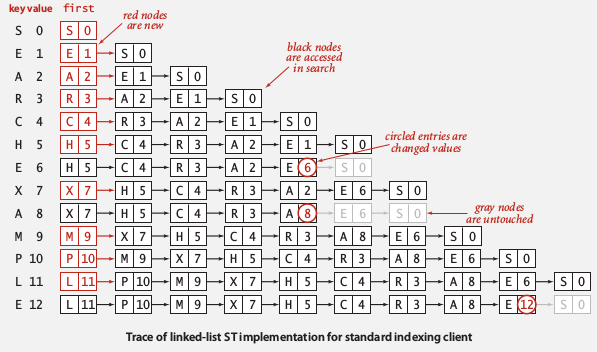
using unordered linked list
ListNode{key, value, next}
- search: scan through all keys ~N
- insert: scan through, if not found, add to front ~N
using ordered array
using 2 arrays: keys[] (sorted), vals[]
⇒ can improve performance by binary search
search operation
write a function rank() that returns the number of keys < k searched.
找不到的时候: 比k小的元素个数=lo (lo>hi, 可以想想当hi=lo以后是怎么移动的)
private int rank(Key k){
int lo=0, hi=keys.length-1;
while(hi>=lo){
int mid = lo + (hi-lo)/2;
int cmp = keys[mid].compareTo(keys[k]);
if(cmp==0) return mid;
else if(cmp>0) hi = mid-1;
else lo = mid+1;
}
return lo;
}
Using rank() to implement the get() method:
public Value get(Key k){
int rk = rank(k);
if(rk<N && keys[rk].compareTo(k)==0) return vals[rk];
return null;
}
insert operation
Like insertion sort, time complexity is ~N for each insert.
summery:
3. Ordered Opeartions
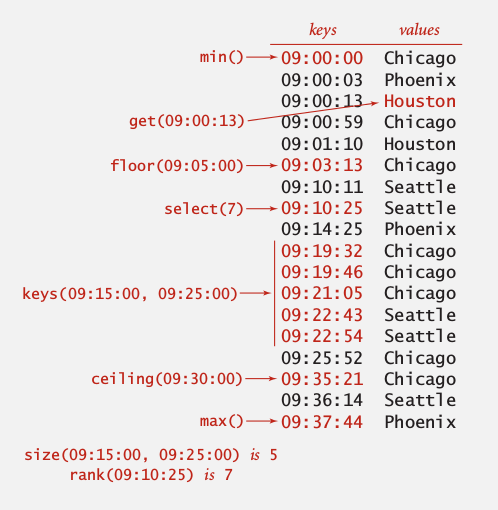
When keys are comparable ⇒ provide more functionalities in the API.
for example:
min()/max(): min/max keydeleteMin()/deleteMax()floor(Key k)/ceiling(Key k): largest key <=k / smallest key >=krank(Key k): nb of keys < keyselect(int i): key with rank=iIterator<Key> keys(lo, hi): iterates through [lo, hi]

Part 9 of series «Algorithms Princeton MOOC I»:
- [Algorithms I] Week 1-1 Union-Find
- [Algorithms I] Week 1-2 Analysis of Algorithms
- [Algorithms I] Week1-Lab: Percolation
- [Algorithms I] Week 2-1 Stacks and Queues
- [Algorithms I] Week 2-2 Elementary Sorts
- [Algorithms I] Week 3-1 Mergesort
- [Algorithms I] Week 3-2 Quicksort
- [Algorithms I] Week 4-1 Priority Queue
- [Algorithms I] Week 4-2a Elementry Symbol Tables
- [Algorithms I] Week 4-2b Binary Search Trees
- [Algorithms I] Week 5-1 Balanced Search Trees
- [Algorithms I] Week 5-2 Geometric Applications of BSTs
- [Algorithms I] Week 6 Hash Tables
Disqus 留言