This week, we'll cover traits, and we'll learn how to organize classes into hierarchies. We'll cover the hierarchy of standard Scala types, and see how to organize classes and traits into packages. Finally, we'll touch upon the different sorts of polymorphism in Scala.
3.1 - Class Hierarchies
abstract class
abstract class IntSet {
def incl(x: Int): IntSet
def contains(x: Int): Boolean
}
abstract class:
- contains members without implementation
- cannot be created with
new
class Extensions
implement the integer set abstract class with BST
2 types of trees: Empty and NonEmpty
class Empty extends IntSet {
override def incl(x: Int): IntSet = new NonEmpty(x, new Empty, new Empty)
override def contains(x: Int): Boolean = false
}
class NonEmpty(elem: Int, left: IntSet, right: IntSet) extends IntSet {
override def incl(x: Int): IntSet =
if (x == elem) this
else if (elem > x) new NonEmpty(elem, left.incl(x), right)// immutable!
else new NonEmpty(elem, left, right.incl(x))
override def contains(x: Int): Boolean =
if (elem == x) true
else if (elem > x) left.contains(x)
else right.contains(x)
}
root class of all classes: Object
replace concrete defintion of super class: override is mandantory.
Object
in the previous example, seems only one single Empty set is needed.
⇒ define Empty as singleton object
no other Empty instances can be created, object is a value.
object Empty extends IntSet {
override def incl(x: Int): IntSet = new NonEmpty(x, Empty, Empty)
override def contains(x: Int): Boolean = false
override def toString = "."
}
Program
create standalone scala applicatoins.
Each such applications contains an object with a main(args:Array[String]) method
exercice: implement union
union(other:IntSet): IntSet
override def union(other: IntSet): IntSet =
left union (right union (other incl elem))
why this recursive call terminates ?
every call to union is on a smaller IntSet !
写成这样就会stackoverflow: other.incl(elem).union(left).union(right)
讨论见: https://www.coursera.org/learn/progfun1/discussions/weeks/3/threads/AzJ-4CLYEeag6wpD-92Rcw
(需要点"view earlier replies"才有)

Dynamic Binding
behavior depends on the runtime type of the object.
~ higher-order functions
Lecture 3.2 - How Classes Are Organized
package
// named imports
import week3.Rational
import week3.{Rational, Hello}
// wildcard import
import week3._
can import either from a package or from an object
automatically imported in scala:
 ex:
ex:

scaladoc: http://www.scala-lang.org/files/archive/api/current/#package
Traits
in scala/java, a class has only one super class (single inheritance).
have several supertypes? ⇒ trait!
- one class can extend many traits (concated by
with) — like javainterface

- traits can contain fileds and concrete methods
- on the other hand, traits cannot have (value) parameters, but classes can
scala class hierchy
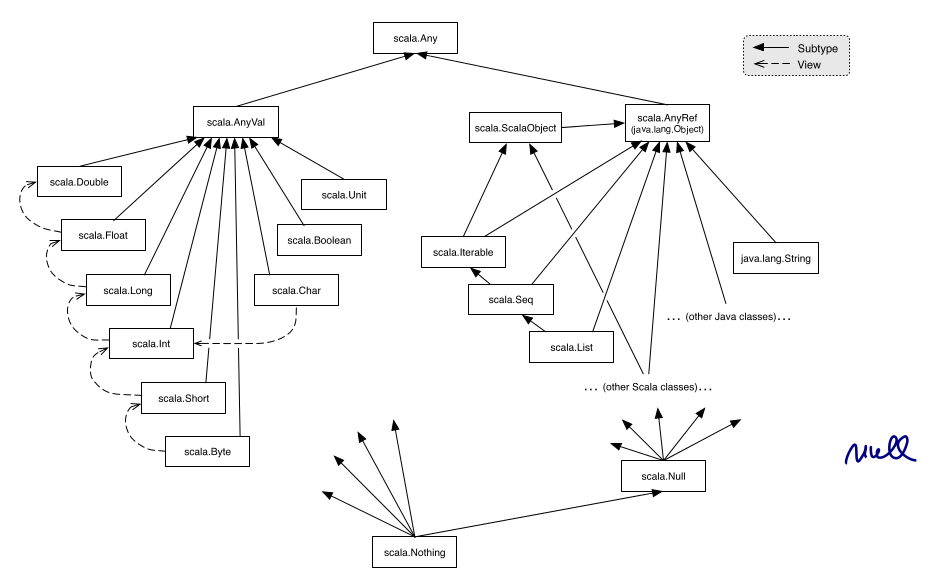
Any: base class of allAnyVal: primitive types (Int, Unit, Boolean,...)AnyRef: (=alias ofjava.lang.Object) all reference types (String, List, Seq, Iterable,...)Nothing: bottom of the hierchy, is subtype of every typeNull: subtype of every reference type,null's type isNull, not compatible withAnyValtypes.
exception: throw Exc, the typeof Exc is Nothing
exercice:
if (true) 1 else false ⇒ type = AnyVal
Lecture 3.3 - Polymorphism
cons-list
immutable linked list

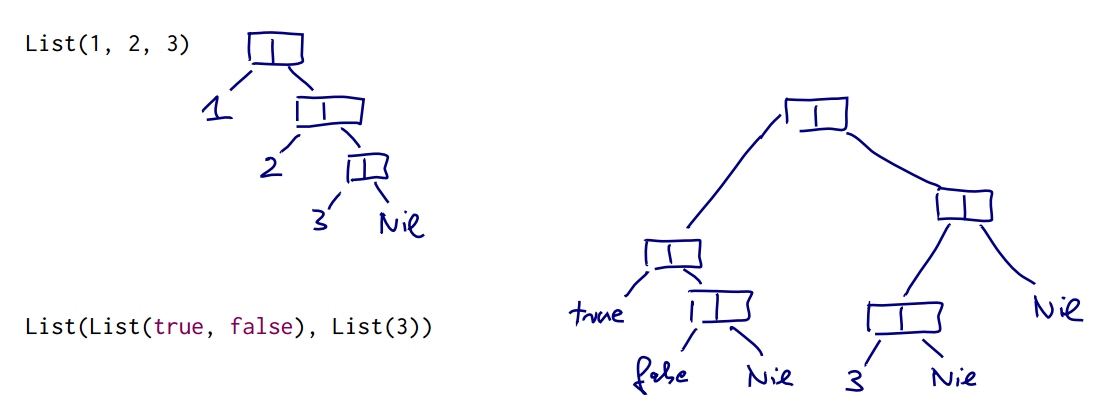 implement this in scala:
implement this in scala:

the val in the class definition: defines at the same time parameter and field of a class, equivalent to:

type parameters (generic)

trait List[T]{
def isEmpty : Boolean
def head: T
def tail: List[T]
}
class Cons[T](val head:T, val tail: List[T]) extends List[T] {
def isEmpty(): Boolean = false
}
head and tail are implemented in the parameters(fields), difference between val and def only consist in the initialization (CBN, CBV).
class Nil[T] extends List[T]{
def isEmpty = false
def head: Nothing = throw new NoSuchElementException("Nil.head")
def tail: Nothing = throw new NoSuchElementException("Nil.tail")
}
use nothing as return type, and throw an exception.
generic functions
type parameters can be applied to functions.
 sometime the type parameter can be deduced by scala compiler.
sometime the type parameter can be deduced by scala compiler.
ex. singleton(2); singleton(true)
Types and Evaulation
type parameters don't affect evaluation.
can assume type parameters are removed before the evaluation (type erasure).
Polymorphism
- subtyping: instances of subclass can be passed to a base class
- generics: function/class with type parameters
exercice: write a function nth(n: Int, list: List)
def nth[T](n: Int, list:List[T]): T =
if(list.isEmpty) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException()
else if (n==0) list.head
else nth(n-1, list.tail)
Programming Assignment: Object-Oriented Sets
TweetSet: an abstract class TweetSet with two concrete subclasses,Empty which represents an empty set, and NonEmpty(elem: Tweet, left: TweetSet, right: TweetSet), which represents a non-empty set as a binary tree rooted at elem. The tweets are indexed by their text bodies: the bodies of all tweets on the left are lexicographically smaller than elem and all bodies of elements on the right are lexicographically greater.
Disqus 留言