RELATIONAL DATABASE
review: key data management concepts:
- data model
- schema
- relational data model
structured data: have a specific schema to start with
relationl database: a set of relations. 2 parts to a Relation:
- schema: name of relation, name and type of columns
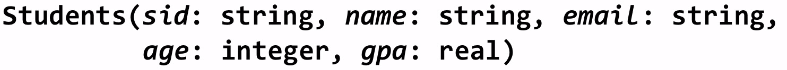
- instance:
any data at given time (cardinality:=nb of rows, degree:=nb of fields)
LARGE DATABASES
RELATIONAL DATABASE EXAMPLE AND DISCUSSION

cardinality=3
degree=5
advantages of Relational Databases:
- well-def structure
- maintain indices for high performance
- consistancy maintained by transactions
disadvantages:
- limited, rigid structure
- most disk space taken by large indices
- transactions are slow
- poor support for sparse data(which is common)
STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE (SQL)
supported by DataFrame of pyspark

JOINS IN SQL
 cross join: carteian product
cross join: carteian product
EXPLICIT SQL JOINS
 explicit version is preferred
explicit version is preferred
TYPES OF SQL JOINS
⇒ controls how unmatched keys are handled
LEFT OUTER JOIN: keys appearring in left table but not in right table will be included with NULL as value
JOINS IN SPARK
- for spark DataFrame: support inner/left outer/semi-join
- for pair RDDs: support inner join(), leftOuterJoin(), fullOuterJoin()
join ex:


outerjoin ex:

fullouterjoin ex:

Lab 2 - Web Server Log Analysis with Apache Spark
Apache Common Log Format (CLF):
127.0.0.1 - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:01 -0400] "GET /images/launch-logo.gif HTTP/1.0" 200 1839
Row(
host = match.group(1),
client_identd = match.group(2),
user_id = match.group(3),
date_time = parse_apache_time(match.group(4)),
method = match.group(5),
endpoint = match.group(6),
protocol = match.group(7),
response_code = int(match.group(8)),
content_size = size
)
- distinctByKey
一个pair RDD按照key来distinct不知道有没有distinctByKey之类的东西, 只好写成这样, 不知是不是对的:
dayHostCount = dayGroupedHosts.map(lambda group : (group[0], len(set(group[1])) ) )
...总体来说很有意思的一个lab...
Disqus 留言